Washington: State public health officials of Washington have pinpointed the origin of the recent listeria outbreak that has raised concerns for milkshake lovers. Following the illness of six individuals who consumed milkshakes at a burger restaurant in Tacoma, Washington, officials have identified Listeria monocytogenes, a strain of bacteria, as the contaminant responsible. Tragically, three people died in the incident and three others are currently undergoing treatment.
The bacterial infection caused by Listeria monocytogenes, is known as listeriosis, which can occur through the consumption of contaminated food items. The infection can lead to direct impacts on the bones, joints, chest, and abdomen, with potentially fatal consequences if left untreated.
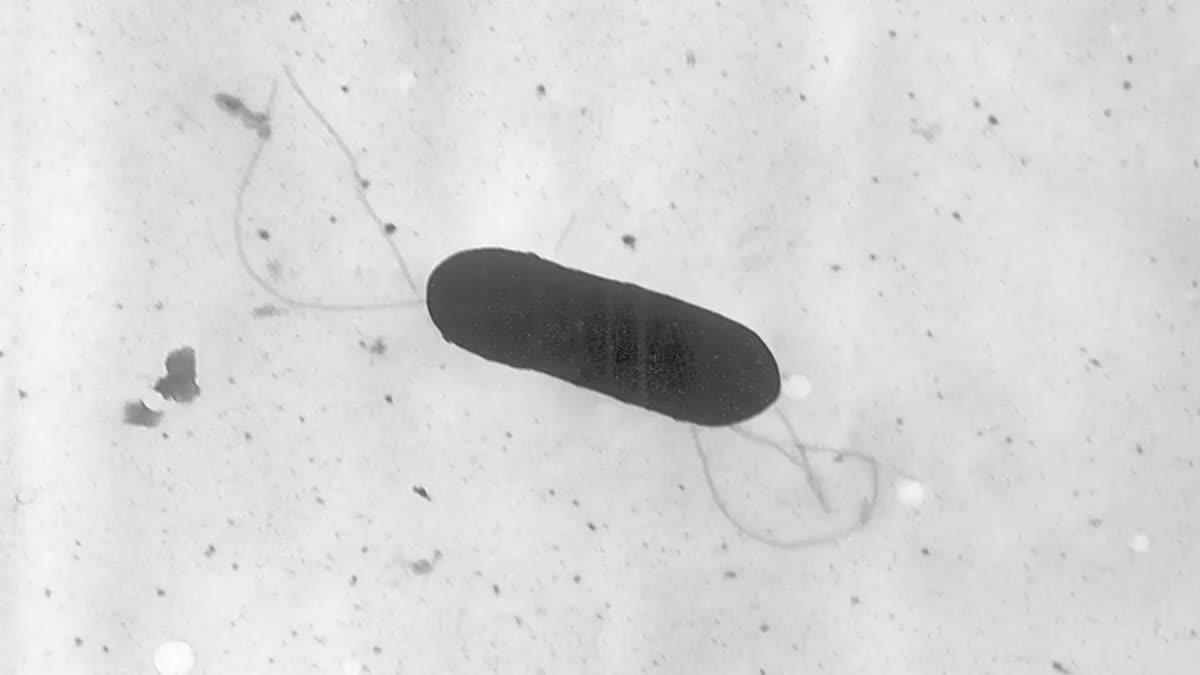
What is Listeria?
Listeria is a bacterium that affects both humans and other mammals, with heightened prevalence in vulnerable groups such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly. These demographics possess weaker immune systems, necessitating heightened dietary vigilance to avert the adverse effects of listeriosis.
The infection normally develops in individuals whose immune systems are weak or impaired, such as newborn infants, pregnant women, the elderly, and those whose immune systems have been compromised by an underlying disease or by immunosuppressive drugs. The disease may appear as a mild influenza-like illness and go unrecognized. In adults meningitis is the most commonly recognized clinical manifestation of listeriosis; the bacterium can also cause endocarditis (inflammation of the heart lining), septicemia (blood poisoning), and skin lesions. Intrauterine infection of the fetus may result in miscarriage, premature birth, or stillbirth; if the infant is born alive, it may develop septicemia or meningitis. Listeriosis responds to treatment with antibiotics.
Symptoms of Listeriosis:
Listeriosis, typically transmitted through contaminated food, manifests in symptoms such as muscle pain, fever, headaches, and dizziness.
Precautions:
- Keeping caution during the consumption of dairy products, raw vegetables, and meats is crucial.
- Adequate cooking
- Thorough cleaning of refrigerator contents
- Prioritizing hygienic dining environments
The above mentioned points are essential to curb Listeria monocytogenes growth, particularly during rainy seasons or in low-temperature conditions, where bacterial proliferation is more likely.