Hydearbad: Radiology is an important part of medical care today. The field developed relatively quickly in the 20th Century, and thanks to computer technology and artificial intelligence (AI), is still advancing. Radiology is a term that almost everyone is well acquainted with as it holds immense importance in the detection as well as treatment of a broad spectrum of medical conditions and touches almost all the specialities like orthopaedics, cardiology, oncology, rheumatology, gastroenterology etc.
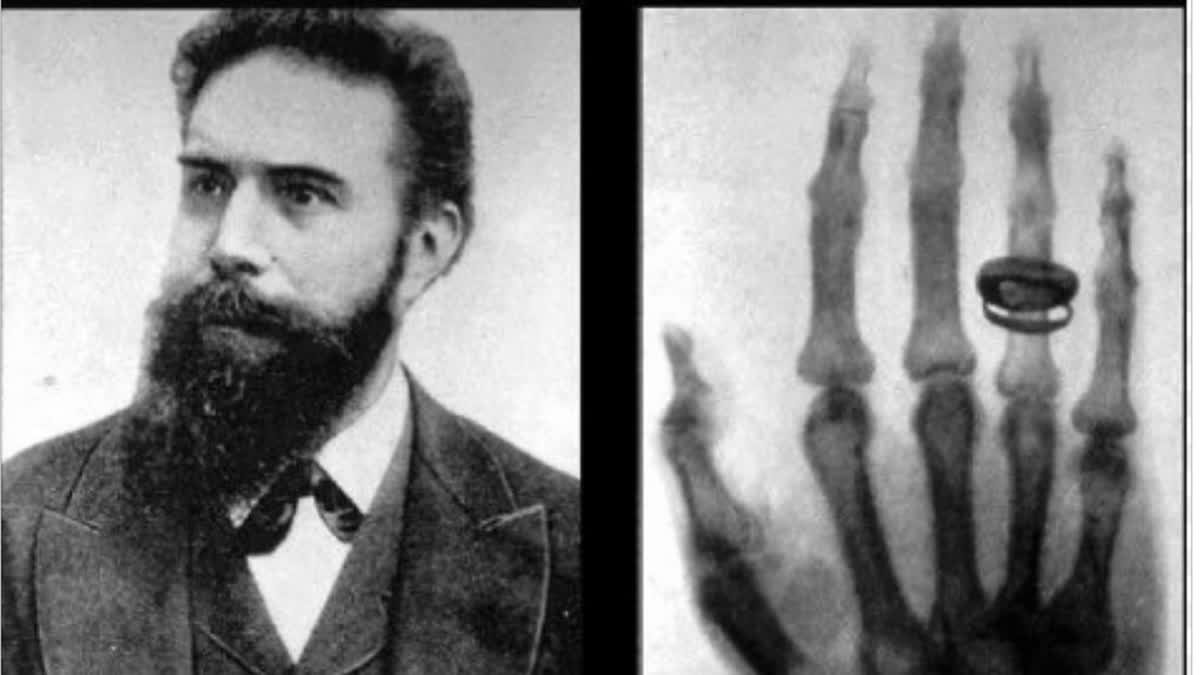
Radiology contains group of imaging techniques that play a pivotal role in the diagnosis, assessment, evaluation and treatment of various medical conditions. Radiology is one of the youngest branches of medicine with a history of around 100 years. It all began with the discovery of X-Rays by Prof Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen in the year 1895, the news of which spread like wildfire.
Rontgen spent the next few weeks studying and researching about the same and found out that these X-rays could easily pass through human tissues and hence could help to detect any foreign particles in the body. The rays would create images of objects of different thicknesses. At one point, his wife put her hand over the photographic plate; the X-ray image showed the bones of her hand and the ring she was wearing, surrounded by a faint outline created by her flesh. It was the first x-ray of a human body part.
It was a miraculous discovery that faced a lot of praises as well as criticism as the harmful effects of these X-rays soon came into light. With further studies and development, most of the risks were evaded and X-rays were started to be used in clinical practice. This further led to the development of endoscopy, mammography, radiation oncology, nuclear medicine and various catheter-based interventions.
The last three decades of the 20th century have seen a paradigm shift in the scope of radiology with the advent of modern imaging modalities like Ultrasound, Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) all of which are offered in most of the hospitals in India.
Types of Radiology:
1. Diagnostic radiology: It involves a broad spectrum of imaging techniques to see the various structures and organs inside the body to determine the root cause of your problem, monitor the progress of your treatment and conduct various screenings. Some of the most common procedures include:
Computed Tomography (CT) scan.
Fluoroscopyfor obtaining real-time moving images of the internal organs.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
Mammography for breast screening.
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA).
Nuclear Medicine.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging/scan. PET combined with CT scan can be used for the detection of various malignancies.
Ultrasound.
Also read: ChatGPT 4 excels at picking the right imaging tests: Study
2. Interventional radiology-
Interventional radiology is a super speciality branch after completing the regular broad speciality Diagnostic Radiology course. It involves the use of imaging guidance to administer medical therapies with the help of catheter, wires and needles. This involves tiny keyhole incisions and use of special dye that help to generate clearer images.
Interventional radiology has proved to be a boon for cancer patients. The procedures can be performed under moderate sedation. Some of the most common interventional radiology procedures include:
Angiography/angioplasty and stent placement in patients with narrowed or blocked arteries to evaluate the extent of blockage and clear it.
Embolization to stop the flow of blood in a particular area of the body to treat a tumour or aneurysm.
Radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, or microwave ablation to burn tumours.
Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty to treat vertebral compression fractures.
Needle biopsies of different organs, like lungs, uterus etc. to detect any abnormality or malignancy.
Breast biopsy for breast cancer.
Uterine artery embolization to halt blood flow to the uterine.
Feeding tube placement in patients who are not able to swallow their food.
Venous access catheter placement, such as ports and PICCs.
As per the latest senses With just approximately 20,000 radiologists serving a population of over 1.4 billion, India is confronted with an alarming ratio of one radiologist for every 1,00,000 individuals, far below global healthcare standards.
How to overcome the shortage?
Technology in the form of teleradiology can play an important role in increasing the access to the subspecialist radiologist by bringing images to them instead of vice versa. Radiological investigations help with an accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and prognostication of diseases. This positively influences treatment decisions, outcomes, referral pathways, and health resource allocation.
However, setting up a radiology service is resource intensive. Sixty percent of our population live in rural areas and their access to health care, high-quality diagnostics, and specialist opinion remain difficult. There is an inequitable distribution of radiology facilities in the country with most of the trained radiologists being concentrated mainly in larger cities and towns.
There are too few radiologists for a population of 1.4 billion. For a long time now, teleradiology has been one of the effective solutions for bridging these gaps between demand and supply. There is an increased appetite for technology adoption by radiology services across the country to meet the demands placed on them.
Picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) and radiology information systems (RIS) have tremendously increased the efficiency, productivity, and throughput of imaging services. Improved connectivity through internet and mobile technology, teleradiology, artificial intelligence, developments in medical imaging informatics, and portable or mobile medical imaging devices have the potential to enable remote locations within the country to gain access to better health care and diagnostics.
To conclude, teleradiology, particularly when combined with artificial intelligence-based algorithms and mobile digital imaging units can address shortages of radiologists; improve access to health; strengthen programs aimed at population screening for the detection and early diagnosis; and emergency care. Alongside the large-scale implementation of teleradiology services for primary healthcare, there is an urgent need to address shortages of radiologists and technicians who can support the service.