New Delhi: Consumer price index (CPI) based retail inflation eased marginally to 3.15 per cent in July on the back of softening fuel and light prices, even as inflation in the overall food basket moved up, government data showed on Tuesday.
Retail inflation was 3.18 per cent in June 2019, while it stood at 4.17 per cent in year-ago period (July 2018).
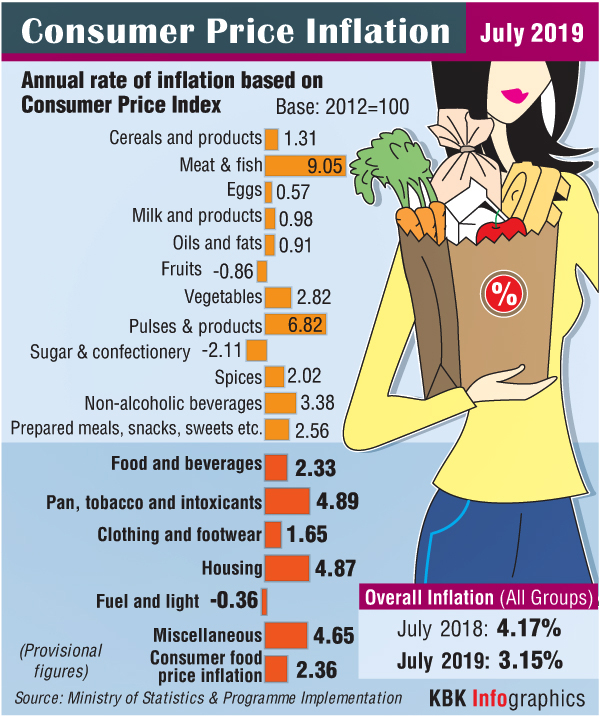
The overall food inflation, measured on consumer food price index (CPFI), moved up to 2.36 per cent during July from the revised 2.25 per cent print for June 2019, as per data released by the Central Statistics Office (CSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
The rate of price rise in vegetables softened to 2.82 per cent during the latest month as against a rise of 4.66 per cent in June, while prices of 'pulses and products' went up to 6.82 per cent from 5.68 per cent.
In case of fruits, the price trend showed upside movement with an inflation print of (-) 0.86 per cent as against (-) 4.18 per cent a month earlier.
Prices of protein rich 'meat and fish' rose at nearly the same level at 9.05 per cent (from 9.01 per cent in June), however, inflation in eggs eased to 0.57 per cent (against 1.62 per cent).
In fuel and light category, deflation was witnessed with a print at (-) 0.36 per cent, as against a rise of 2.32 per cent a month ago.
Read more:Banks report a reduction in NPA; seek steps to address stress in NBFCs: FICCI
"The marginal dip in the CPI inflation in July 2019 was led by fuel and light, which recorded a disinflation in that month, even as food and core inflation inched up.
"The incoming trends in food prices need to be cautiously watched, following the recent flooding in some states, rising vegetable prices and continued lag in kharif sowing. Moreover, an unfavourable base effect is likely to contribute to a hardening of food inflation in the ongoing quarter," said Aditi Nayar, Principal Economist, Icra.
Retail inflation remains subdued with most of the components indicating not much variation compared to the earlier periods, said Joseph Thomas, Head Research- Emkay Wealth Management.
"But, we need to make allowance for factors like a cheaper Rupee, loss of crops due to heavy rains and the consequent effects on prices, while trying to judge the future inflation levels," he added.
Nayar said the core-CPI inflation may not ease meaningfully from the current levels, as demand for services will remain sticky even during an economic slowdown.
At present, we expect the CPI inflation to inch up in the next two months, while remaining below the MPC's target of 4 per cent during second quarter of FY2020.
"The CPI inflation trajectory may allow for a 15 bps rate cut in October 2019, after monsoon related uncertainties get resolved, especially if crude oil and other commodity prices remain relatively soft," she added.
As per the latest sowing data maintained by the Union Agriculture Ministry, total acreage sown to all Kharif crops so far has remained lower at 869.55 lakh hectare as against 918.70 lakh hectare in the year-ago period.
Agriculture Secretary Sanjay Agrawal on Friday said that the deficit in overall sowing area has improved compared to the previous week and the gap has come down.
Currently, the retail inflation is well below the RBI's comfort level. The government has asked the central bank to keep inflation in the range of 4 per cent.
The Reserve Bank of India mainly factors in retail inflation in its bi-monthly monetary policy.



