Hyderabad: Microorganisms or Microbes (Algae, Bacteria, Fungi, and Protozoa) are found everywhere. They are capable of growing on sources like air, water, soil, food products, and on any place where nutrients are available. This property of microbes is exploited in many ways that in turn are useful for humans and animals. Mainly in the food industry, the role of Bacteria and Fungi is immense.
Also Read: Microorganisms or microbes in our day to day life
Microbes when growing on the foods, either produce beneficial results or cause spoilage of food. The beneficial results include their role in the production of:-
- Acids (citric acid, lactic acid, etc)
- Alcohols (ethyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, etc)
- Dairy products (cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, butter, etc)
- Bakery products (bread etc).
Spoilage of food by the microbes includes changes in color and odor making it unsuitable for human consumption. The mushy growth on bread and the slimy texture of meat are few examples.

Visalakshi Arigela has done her graduation and post-graduation in Microbiology. She is answering a simple question; Have you ever thought that microscopic creatures are actually involved in the production of foods? Yes. The bacteria and fungi release some of the byproducts like alcohols, acids, antibiotics, enzymes, etc in the absence of oxygen. This process is called fermentation.

Visalakshi is explaining with some examples where the microbes ferment the foods.
When we add curd to the milk, the lactic acid bacteria grow on the milk and convert the milk into curd. The lactose in the milk gets converted into lactic acid. Lactose------fermentation-------lactic acid.
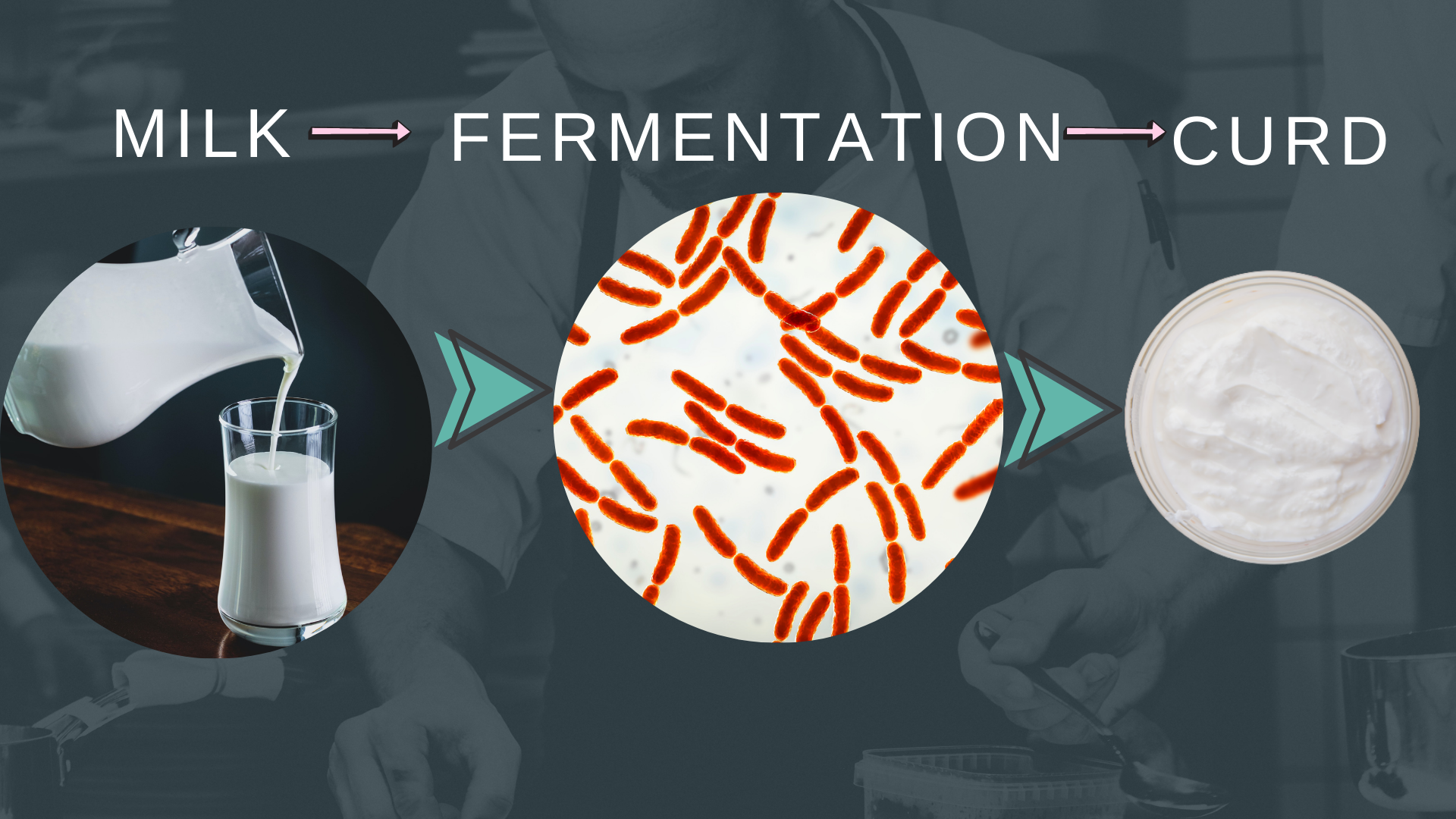
Streptococcus lactis and Lactobacillus fermenti are some of the examples of lactic acid-producing bacteria. These bacteria are mostly involved in the fermentation of dairy products.

In some food varieties like idly, dosa, dhokla, naan, bhatura, etc, we can see a rise in the batter/dough with a typical odor when kept for few hours to overnight. The raise in batter and sourness is due to the release of acids and carbon dioxide.


Legumes/rice/pulses/wheat---fermentation---lactic acid, ethanol/acetic acid+co2. Visalaksi adds that apart from these foods, cheese, buttermilk, cream, green olives, sauerkraut (shredded cabbage), soibum (fermented bamboo shoots) hawaiijar (fermented soybeans), hentak (fermented fish), vinegar, wine, beer, soy sauce, pickled olives, etc are some more examples of food products where the microbes ferment and enhance the flavor of the foods.

The foods and food products mentioned above are examples of microbial metabolism (fermentation) byproducts. Here come some more varieties of food, where some of the microbes are edible which include mushrooms, single-cell proteins.
Mushrooms are edible fungi that can grow naturally or cultivated. The natural varieties can be found in forests, fields. Cultivated mushrooms include white button mushrooms, oyster mushrooms which are grown on agricultural wastes.
Due to the high protein content in the microorganisms, these can also be used directly as food to animals and humans in some countries. This is called a single-cell protein (SCP). Candida Utilis, Spirulina are some of the examples of SCP.

Their immense role in foods and food products is now understood by everyone. Don’t you now admire the microbes? Yes, we should as they are giving very valuable products. Some of the foods are rich sources of vitamins, minerals, proteins, probiotics, and so on. Their contribution is really vast. As always microbes are known as disease-causing germs, let’s all remember their helping nature to humans also.
You can follow Visalakshi on Facebook @visalakshi.arigela, Twitter @VisalakshiArig1
Also Read: Viruses exist as both living and non living, used in vaccine production



