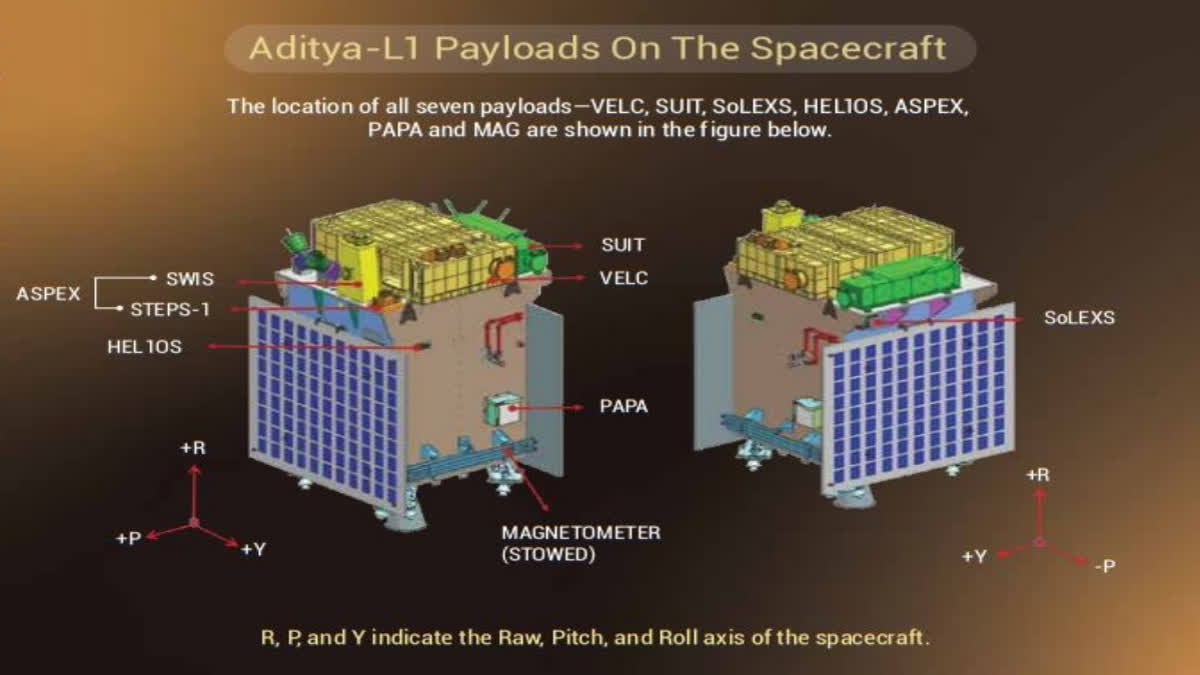
The ambitious mission, Aditya-L1, will carry a payload composed of seven instruments, namely, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), the Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), the High Energy L1 Orbiting Spectrometer (HEL1OS), the Soft X-ray Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEX), the Plasma Analyzer Package for Aditya (PAPA), Aditya Solarwind and Particle Experiment (ASPEX) and a Magnetometer.
The seven payloads
The spacecraft carries seven scientific payloads for systematic study of the Sun. All payloads are indigenously developed in collaboration with various ISRO Centres:

Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) is the prime payload onboard Aditya-L1, designed as a reflective coronagraph with a multi-slit spectrograph. The VELC, developed by Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengalore in close collaboration with ISRO, is designed to study solar corona and dynamics of coronal mass ejections.
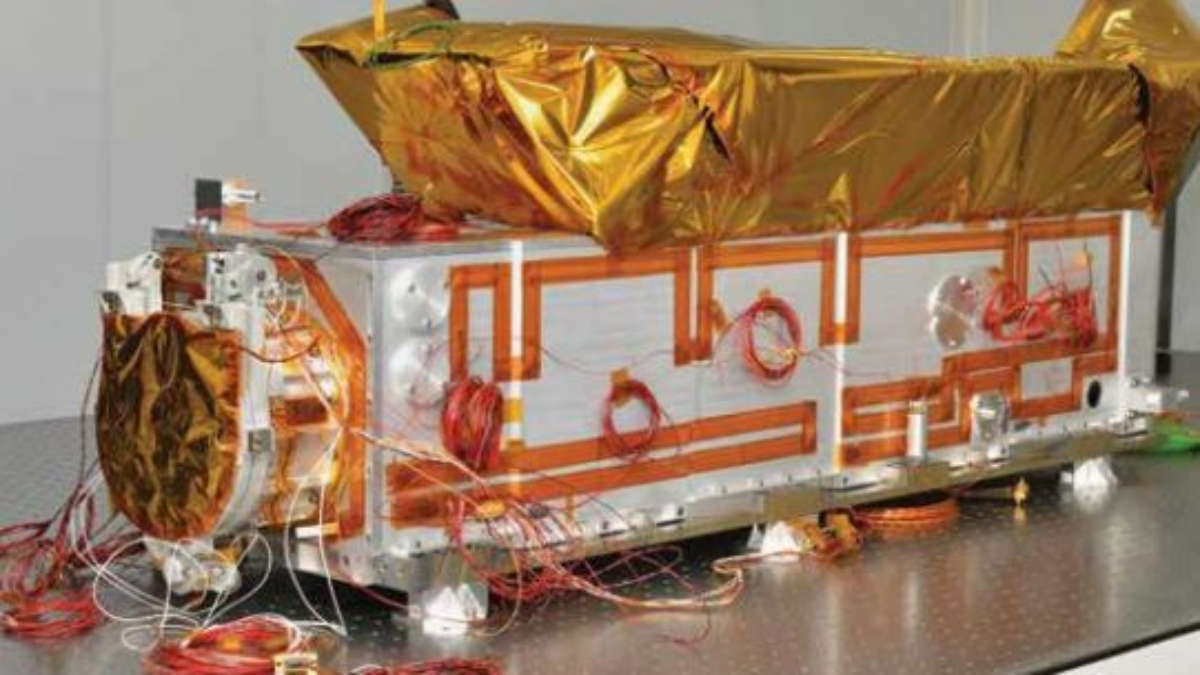

Solar Ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) is a UV telescope to image the solar disk in the near ultra-violet wavelength range. The payload, developed by Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pune in close collaboration with ISRO, will image the Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultra-violet (UV) and, to measure the solar irradiance variations in near UV.
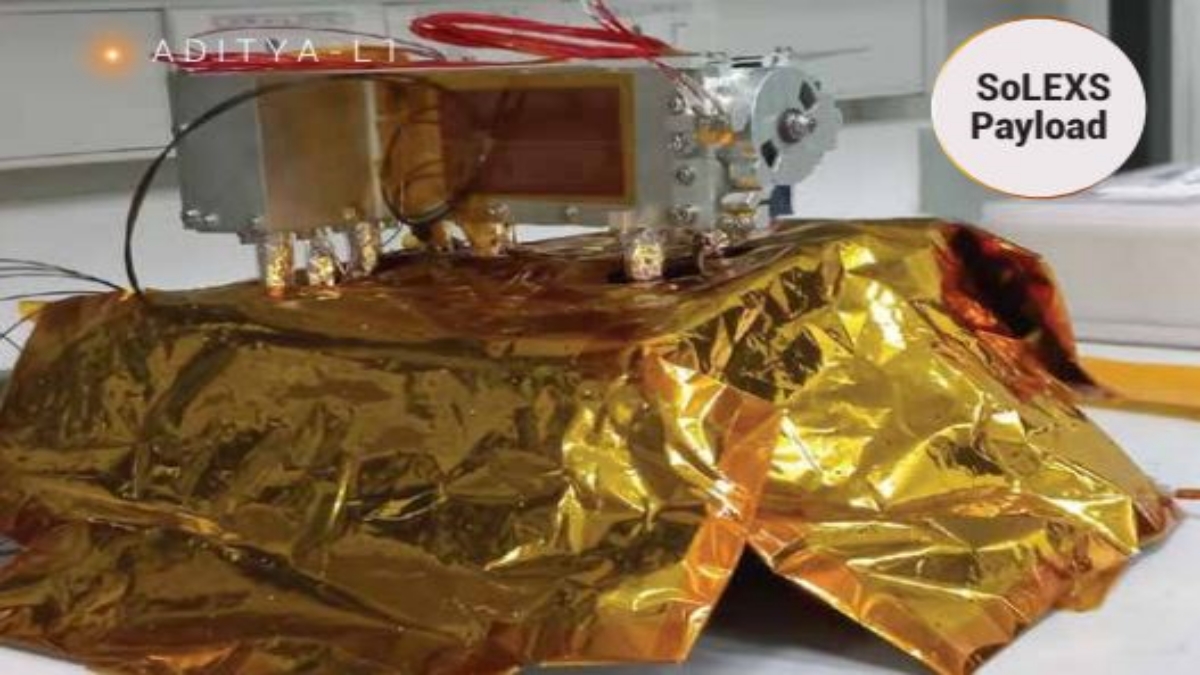

Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) is a soft X-ray spectrometer onboard Aditya-L1. The payload is designed to measure the solar soft X-ray flux to study solar flares.
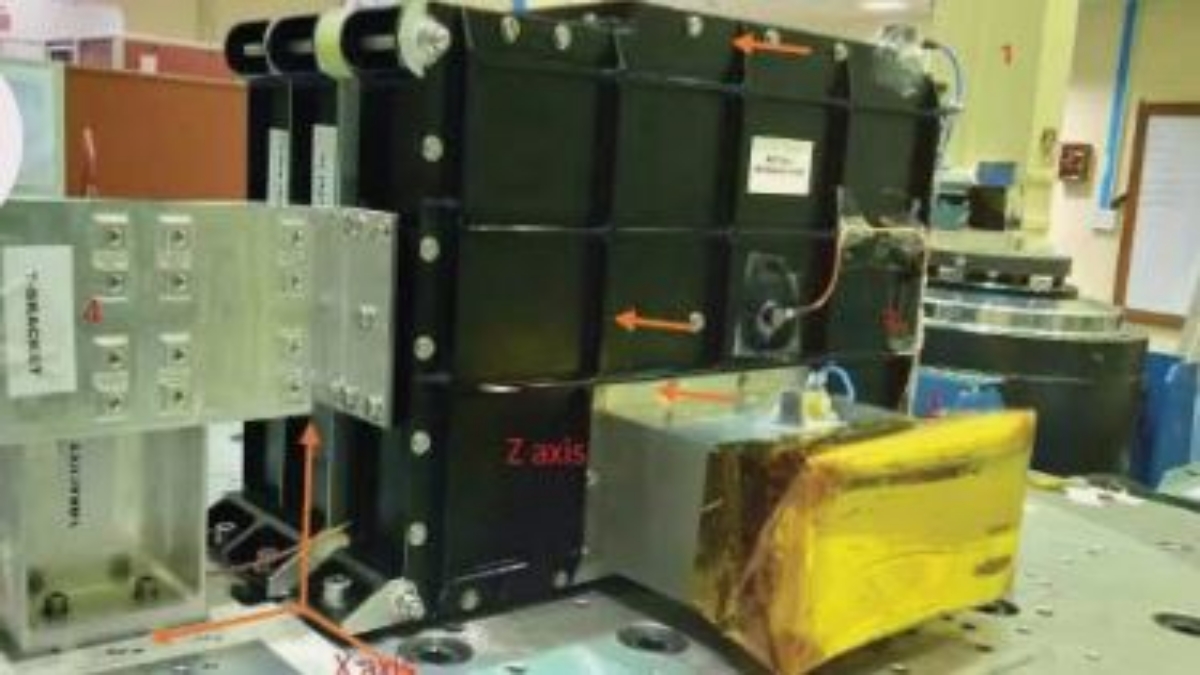

High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) is a hard X-ray spectrometer designed to study solar flares in the high energy X-rays.
Both, SoLEXS and HEL1OS payloads are developed at U R Rao Satellite Centre, Bangalore.
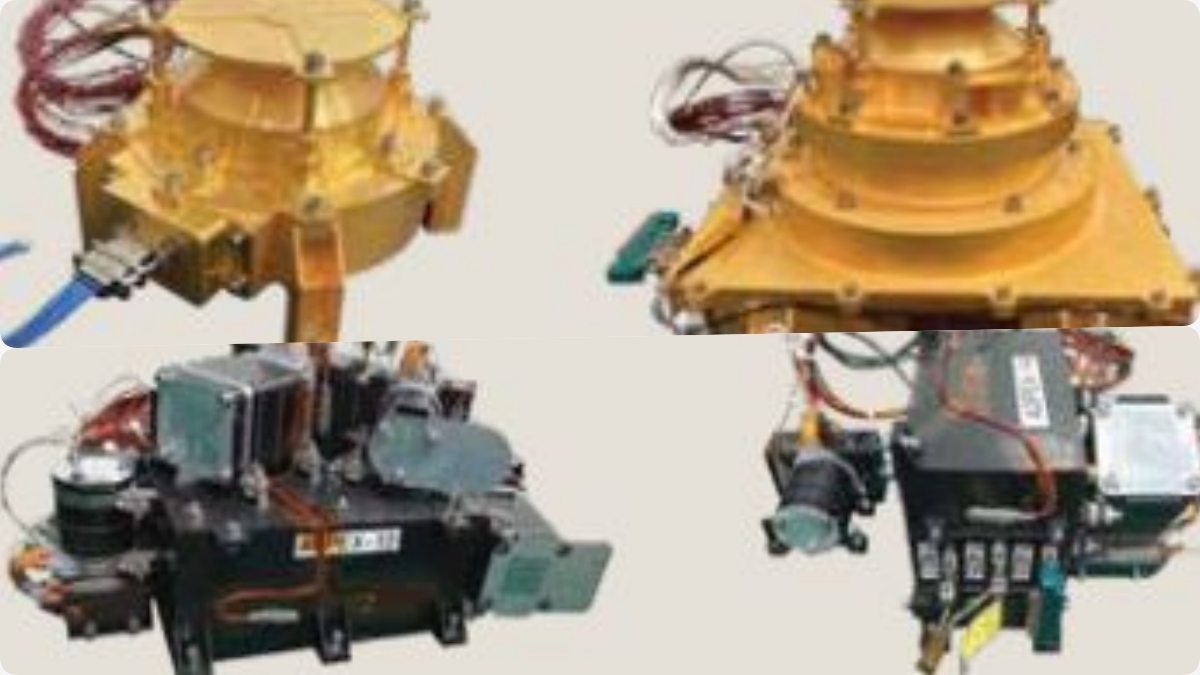

Aditya Solar wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX) payload comprises 2 subsystems: SWIS and STEPS.
SWIS (Solar Wind Ion Spectrometer) is a low-energy spectrometer that is designed to measure the proton and alpha particles of the solar wind.
STEPS (Suprathermal and Energetic Particle Spectrometer) is a high-energy spectrometer that is designed to measure high-energy ions of the solar wind. The payload, ASPEX, is developed at Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad.
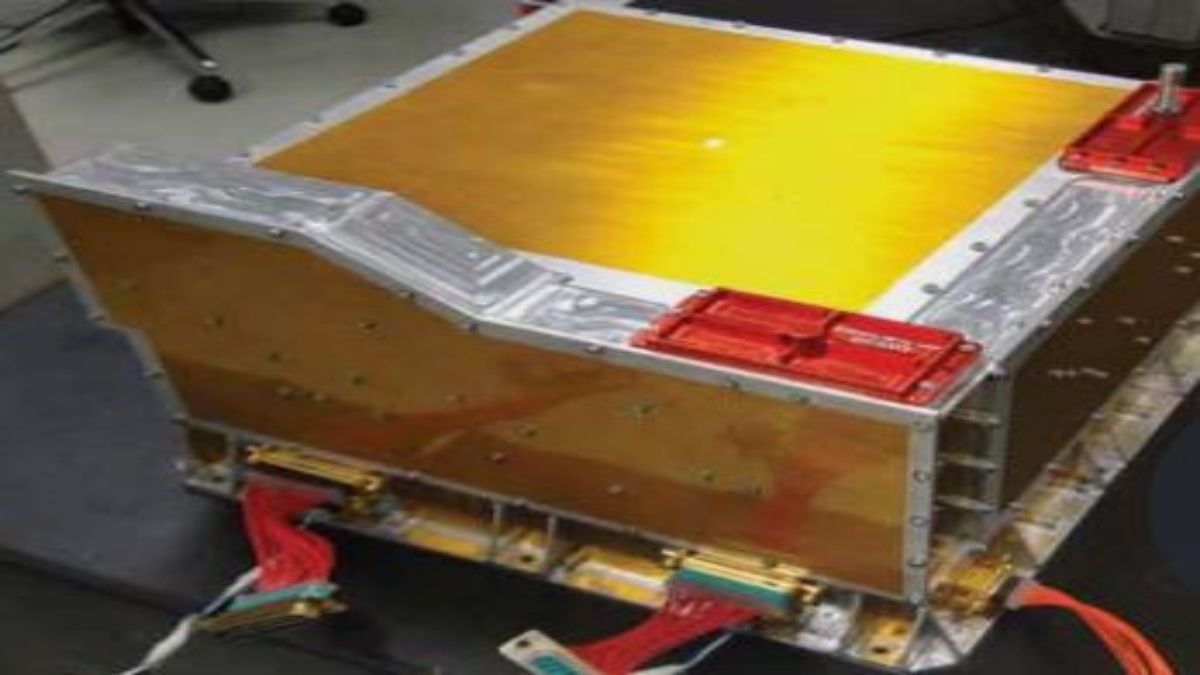

Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) is designed to understand solar winds and its composition and, do mass analysis of solar wind ions. The payload, PAPA is developed at Space Physics Laboratory, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, Thiruvananthapuram.
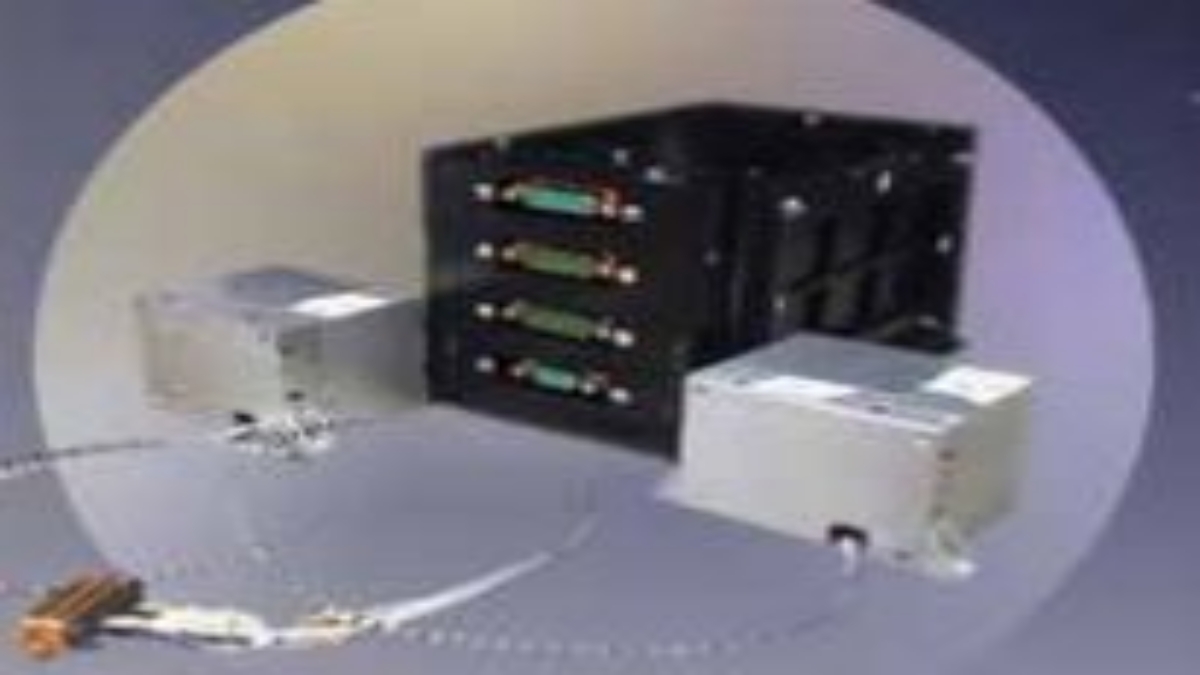

Magnetometer (MAG) onboard Aditya-L1 is meant to measure the low intensity interplanetary magnetic field in space. It has two sets of Magnetic Sensors:one at the tip of a 6 meter deployable boom, and the other in the middle of the boom, 3 meters away from the spacecraft. The payload, developed at Laboratory for Electro Optics Systems, Bengalore, is capable of measuring interplanetary magnetic fields at the L1 point.
As Aditya-L1 embarks on its mission, it is poised to provide a comprehensive measurement of solar radiation across a spectrum spanning from hard X-rays to infrared. Furthermore, it will deliver in-situ measurements of particles within the solar wind, offering a deeper comprehension of the Sun's magnetic field dynamics at the L1 point.
- Explained: All about Aditya-L1's SUIT payload imaging Sun's Photosphere, Chromosphere
- Aditya-L1: India's solar mission launch countdown starts today, says ISRO
- Aditya-L1 ready for launch: ISRO completes launch rehearsal of solar mission
- Explained: Aditya-L1 mission, India's first space-based observatory to study the Sun