Mumbai: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor Shaktikanta Das on Thursday announced that the monetary policy committee (MPC) has decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 4% while keeping an ‘accommodative’ stance during its bi-monthly monetary policy review.
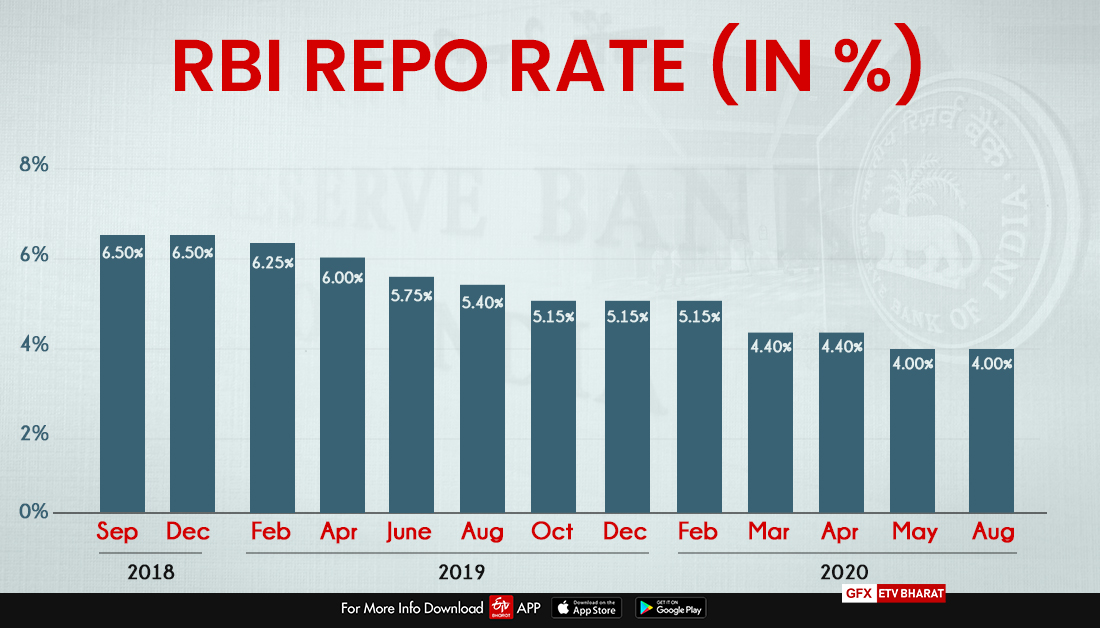
The reverse repo rate also stands unchanged at 3.35%, so do the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate and the Bank rate at 4.25%.
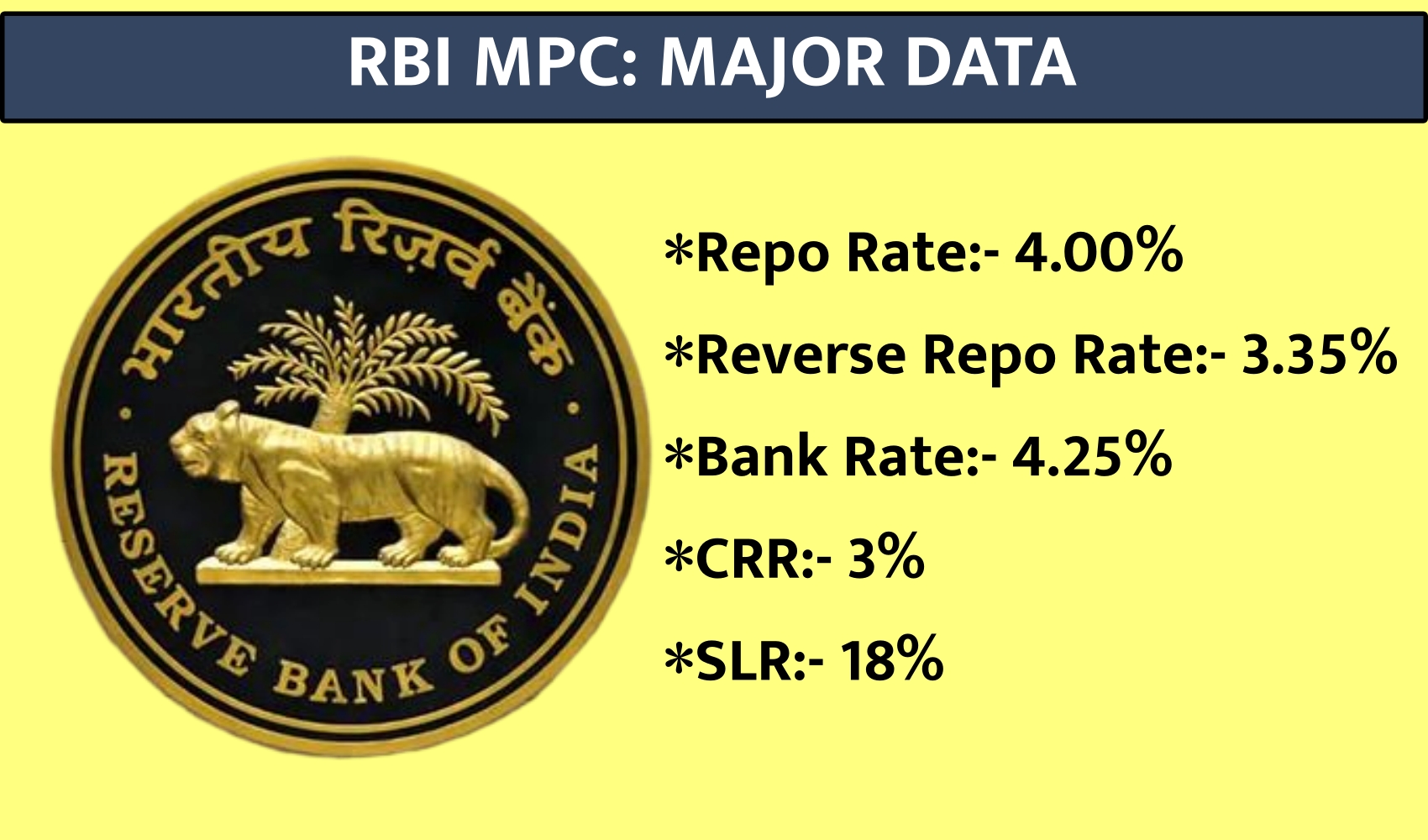
Besides policy rates, RBI made several other important announcements in order to support the recovery of the economy amid the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic. Here’s a quick look at some key decisions:
1) Loan resolution framework
RBI has allowed lenders to restructure loans of corporate and individual borrowers subject to specified conditions.
“It has been decided to provide a window under the June 7th Prudential Framework to enable lenders to implement a resolution plan in respect of eligible corporate exposures - without change in ownership - as well as personal loans, while classifying such exposures as standard assets, subject to specified conditions,” Das said in his statement.

The central bank would be constituting an expert committee headed by veteran banker KV Kamath which shall make recommendations to RBI on guidelines for such resolution plans.
2) Restructuring of MSME debt
RBI said stressed MSME (micro, small and medium enterprises) borrowers will be eligible for restructuring of their debt if their accounts were classified standard as on 1 March 2020.

This restructuring will have to be implemented by 31 March 2021, added RBI.
To recall, in February, the RBI had decided to extend the benefit of one-time restructuring without an asset classification downgrade to standard accounts of GST-registered MSMEs that were in default as on 1 January 2020.
Read more:A New Chapter In Indian Space History
Last week, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman had said that the government is working with the RBI on the need for restructuring of loans to help the industry tide over the impact of COVID-19.
3) Increase in LTV ratio for gold loans
With a view to mitigating the impact of Covid-19 on households, RBI has decided to increase the permissible loan-to-value ratio (LTV) on gold loans to 90%. But, this relaxation shall be available only till 31 March 2021.
As per current guidelines, loans sanctioned by banks against pledge of gold ornaments and jewellery for non-agricultural purposes should not exceed 75% of the value of gold ornaments and jewellery.
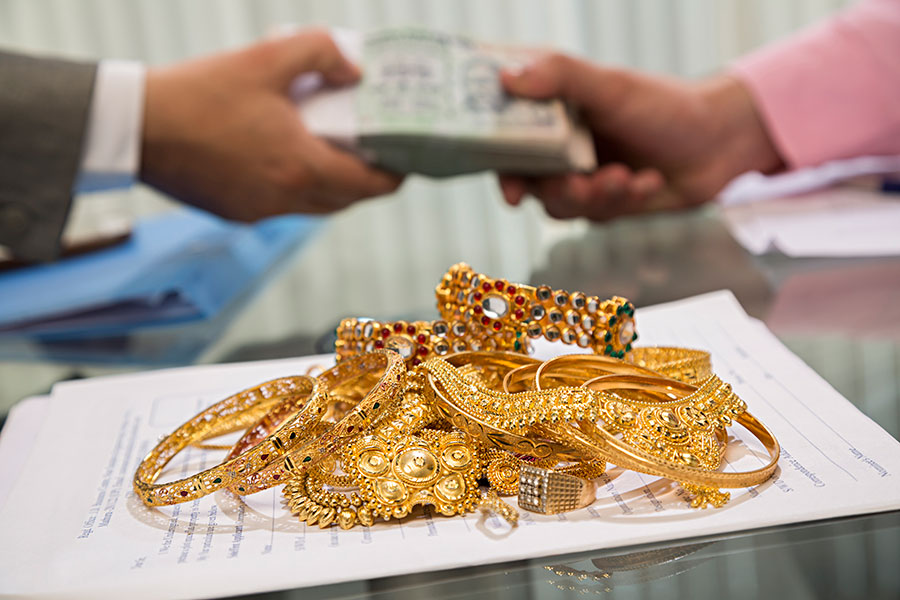

With gold prices touching Rs 55,000 per 10 gm, this could create a huge liquidity window for individuals and households in India where gold holdings in form of jewellery and coins is common.
4) Revision in priority sector lending rules
RBI has also revised the Priority Sector Lending (PSL) guidelines. The central bank now plans to put in place an incentive framework for banks to address the regional disparities in the flow of priority sector credit.
This means that higher weightage will be assigned for incremental priority sector credit in the identified districts having lower credit flow, while a lower weightage would be assigned in identified districts where the credit flow is comparatively higher.
More importantly, the PSL status is also being given to start-ups which can provide a major boost to these firms in terms of access of funds.

To push clean energy projects, the limits for renewable energy, including solar power and compressed bio-gas plants, are also being increased under the priority sector credit framework.
Currently, banks have to keep 40% of Adjusted net bank credit towards PSL.
5) Safeguarding non-cash payments
To enhance safety of cheque payments, RBI decided to introduce a mechanism of Positive Pay for all cheques of value Rs 50,000 and above. This will cover approximately 20% and 80% of total cheques by volume and value, respectively.

Positive pay is essentially an automated cash-management service employed to deter check fraud. Banks use positive pay to match the checks a company issues with those it presents for payment. Any check considered suspect is sent back to the issuer for examination. The system acts as a form of insurance for a company against fraud, losses, and other liabilities.
Moreover, RBI also said online dispute mechanism for digital payments will also be introduced.
(ETV Bharat Report)



