Chennai: Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras Researchers have identified a sustainable and high-yielding alternative source for the anti-cancer drug Camptothecin. This novel microbial fermentation process can be an economically-efficient method of production to fulfil the market demand at a large scale.
Topotecan and Irinotecan are two widely used anticancer drugs, which are produced by using Camptothecin as the lead molecule. More than a dozen derivatives and conjugates of Camptothecin are under various stages of clinical trials for anti-cancer applications.
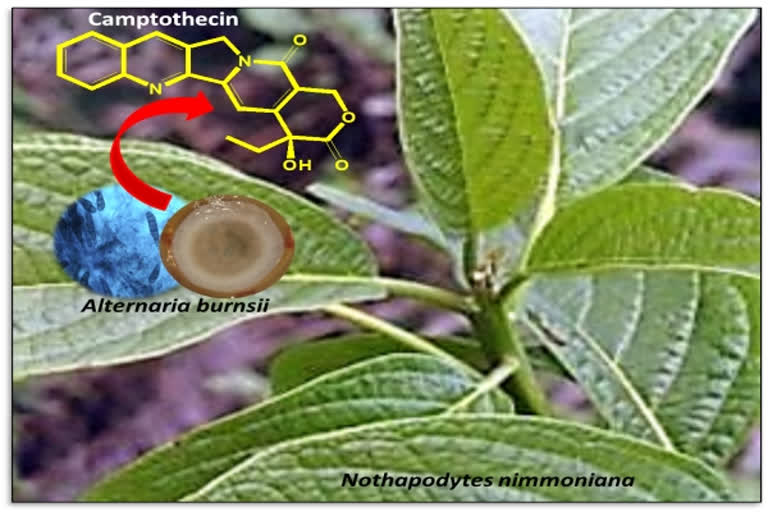
Camptothecin is an alkaloid isolated from the Chinese tree Camptotheca acuminata and the Indian tree Nothapodytes nimmoniana. Nearly 1,000 tons of plant material is required to extract just one ton of Camptothecin. Due to extensive overharvesting to meet the market demand both these plants are now critically endangered. The N. nimmoniana population has seen more than a 20% decline in the last decade alone.
IIT Madras Researchers have now developed an alternative method of Camptothecin production to meet the demand and conserve natural sources. To this effect, they developed a microbial fermentation process that can be an economically efficient and sustainable method of production to fulfil the market demand at a large scale.
The research was led by Dr Smita Srivastava, Associate Professor, Department of Biotechnology, IIT Madras. This work was recently published in the peer-reviewed International Journal of Scientific Reports (a Nature Research Publication).
Also read: IIT-M researchers develop technology to improve braking performance in EVs
Highlighting the applications for this research, Dr Smita Srivastava said, “The novelty of the work lies in the fact that unlike other potential microbial strains reported, this strain has been found to show sustainable production even beyond 100 generations. The plan now is to use the isolated novel strain for the development of a microbial fermentation based sustainable bioprocess for large scale in vitro production of Camptothecin, preferably in collaboration with interested Industrial partner(s).”
Cancer has been a leading cause of death worldwide including in India. It is projected that by 2026, the new cancer cases in India annually would reach 0.93 million in male and 0.94 million in female patients, according to a study published in Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention.