Hyderabad: The deadly coronavirus is affecting vital organs in the body. Unidentified health issues are emerging in people who have long recovered from the infection. In fact, the after-effects are more pronounced in second wave infections. Initially, it was believed that the SARS-nCoV-2 impacted only the lungs. However, it has been identified in several cases recently, that the virus is equally impacting kidneys, liver, and heart. Overdose or misuse of drugs used to treat COVID-19 is also one of the reasons for these consequences. Steroids, antiviral drugs, and painkillers can impair kidney function. What is the impact in the long run? What kind of precautions can be taken? Read on to know what experts have to say.
In the early days of the pandemic, it was thought that the virus affected only the lungs. But more and more patients have been reporting kidney ailments post-recovery. Minor health issues are worsening after the infection. In 20 to 30 percent of people with severe COVID-19 symptoms, or those who had received intensive care or artificial ventilation; acute kidney injuries are being reported. Post recovery, few patients even need dialysis. Besides the virus, the drugs used in treating coronavirus are also impacting organ functions. In the wake of a surge in second wave infections, experts have analyzed the impact of the virus on kidneys, and detailed the precautions to be taken.
The aftermath of kidney damage
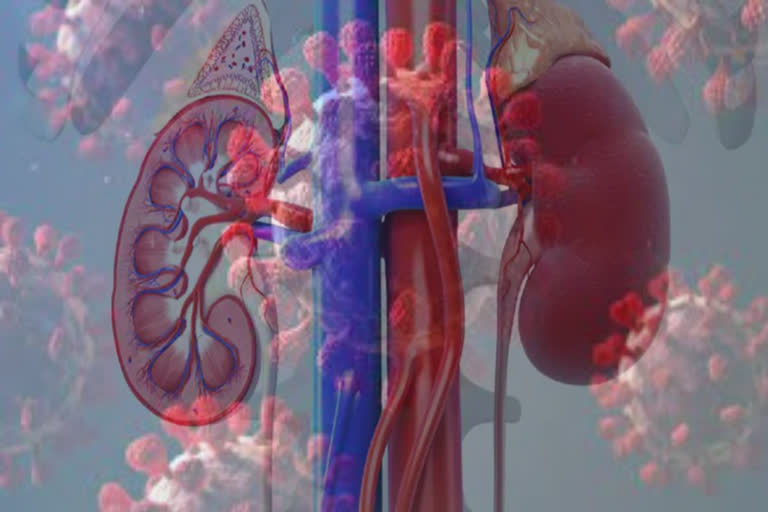
Every organ in the human body is interdependent on each other. Kidney damage can impact the functioning of other organs like the heart, and liver. Kidneys filter out impurities through the functional units called nephrons. Nephrons comprise glomeruli and tubules. Blood goes through glomeruli first. The filtered liquid from the blood then enters the tubules, which absorb essential salts and minerals like sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate. The remaining fluid goes out through the urethra. When the coronavirus attacks kidneys; glomeruli get damaged, and excrete red blood cells and protein in the urine. If tubules get affected, the body’s ability to absorb essential minerals will be compromised. This is called a tubular disorder. If red blood cells and proteins get excreted in the urine for extended periods; the person becomes anemic, or develops edema.
Read: Centre provided over 21 crore COVID-19 vaccine doses to states, UTs so far
Impact of the virus on kidneys
- Initially, it was believed that only 3 to 5 percent of corona patients developed kidney ailments. But studies across various countries identified that the impact of the virus is quite high. In the second wave, the impact is further pronounced. At present, kidney problems are prevalent among recovered patients in Telangana.
- In few patients, the virus is latching on to receptors in the kidneys. The angiotensin-converting-enzyme II (ACE2) receptor on the outer surface of the kidneys acts as gateways for the virus to enter. Kidney function gets impaired when the virus attacks, resulting in a condition called COVID-associated nephropathy (COVAN).
- Kidney function also gets impaired due to a significant drop in oxygen levels in COVID-19 patients.
- Inflammation caused by cytokine storm also damages kidney muscles.
- Steroids and antiviral drugs used in treatment can also have a negative impact.
- Few other medications can also cause kidney damage, lowering blood pressure. This causes septic shock.
- Dehydration is also a major reason for kidney ailments in corona patients. If there is a delay in detection, creatinine levels may shoot up.
- Another major problem with COVID-19 is the formation of clots (thrombosis) in blood vessels. These clots are forming in kidney tubules as well.
- In patients with post-recovery kidney damage, dialysis or kidney replacement therapy may be required. In those with impaired heart function, ECMO support is needed.
Read: NEERI's alternative for collecting sample for RT-PCR test
What nephrologists have to say?
In patients whose kidney membrane is damaged by corona, the condition may return to normal after a while. In those with pre-existing kidney issues, there is a risk of protein excretion in urine. Even post-recovery, it is important to be careful till kidney function is restored. Medication must be continued under doctor supervision. Corona patients are likely to develop body aches from dehydration. So, painkillers should not be used at will. Plenty of water and Electral powder must be taken from time to time. Some of the drugs used to treat high blood pressure can affect ACE2 functioning in the kidneys. Those who are on BP medication must take doctor’s advice first – Dr. Kalyan Chakravarthy, Endocrinologist, and Transplant Physician.
People who got admitted to intensive care, or received high-flow oxygen for severe COVID-19 symptoms, must be careful post-recovery. There is a greater risk of kidney failure in such people. There has been no extensive study about the impact of the virus on kidneys in such cases. Since people with kidney ailments have lesser immunity, they are more prone to contracting the virus. The infection can be life-threatening for people undergoing dialysis, and those with kidney transplants. 20 to 25 percent of fatalities were reported in corona patients with chronic kidney diseases. Since the spread and severity are higher in the second wave, people with co-morbidities must get vaccinated, and follow all the safety precautions. Immunosuppressant drugs are used for a longer time to treat people with chronic kidney disorders. Such people must contact their doctor to know if they must continue or discontinue using those medicines – Prof Dr. T Ravi Raju, Nephrologist, former Director of Medical Education (Andhra Pradesh)
Read: ICMR approves home-based rapid antigen testing kit for COVID-19