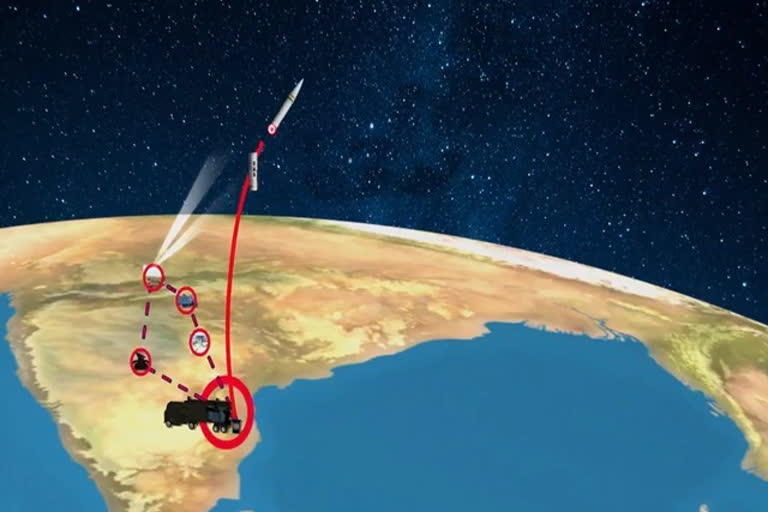
Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Wednesday announced that India had become the fourth country in the world to successfully hit a satellite in space with an anti-satellite missile.
Indian scientists have successfully carried out the test of an anti-satellite missile by bringing down one of its satellites in the low earth orbit 300 kilometres from the Earth’s surface.
But what does this mean and and what relevance does it hold for the country? We have explained it here.
What is Mission Shakti?
On March 27, 2019, India conducted Mission Shakti, an anti-satellite missile test, from the Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island launch complex. This was a technological mission carried out by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The satellite used in the mission was one of India’s existing satellites operating in the lower orbit.The test was entirely successful and achieved all the parameters as per the plans. The test required an extremely high degree of precision and technical capability.
What is the relevance of the test?
The significance of the test is that India has tested and successfully demonstrated its capability to interdict and intercept a satellite in outer space based on complete indigenous technology.With this test, India joins an exclusive group of space faring nations consisting of USA, Russia and China.
Which satellite was used in the mission?
The satellite used was an Indian satellite.
Which missile/interceptor was used?
The DRDO’s Ballistic Missile Defence interceptor was used, which is part of the ongoing ballistic missile defence programme.
There are other ways to demonstrate ASAT capabilities such as "fly-by tests” and jamming. So, why did India use the particular technology of kinetic kill?
This is a technology where India has developed capability. Space technologies are constantly evolving. India has used the technology that is appropriate to achieve the objectives set out in this mission.
Does the test create space debris?
The test was done in the lower atmosphere to ensure that there is no space debris. Whatever debris that is generated will decay and fall back onto the earth within weeks.
Why did we do the test?
India’s space programme is a critical backbone of India’s security, economic and social infrastructure. The test was done to verify that India has the capability to safeguard our space assets. It is the Government of India’s responsibility to defend the country’s interests in the outer space.
Why was the test done now?
The tests were done after India had acquired the required degree ofconfidence to ensure its success, and reflects the intention of the government to enhance national security. India has seen an accelerated space development programme since 2014.
Is India entering into an arms race in outer space?
India has no intention of entering into an arms race in outer space. The nation has always maintained that space must be used only for peaceful purposes. It is against the weaponization of Outer Space and support international efforts to reinforce the safety and security of space based assets.
Besides, India believes that Outer space is the common heritage of humankind and it is the responsibility of all space-faring nations to preserve and promote the benefits flowing from advances made in space technology and its applications for all.
What are the international laws on weapons in outer space?
The Principal International Treaty on space is the 1967 Outer Space Treaty. India is a signatory to this treaty, and ratified it in 1982. The Outer Space Treaty prohibits only weapons of mass destruction in outer space, not ordinary weapons.
India expects to play a role in the future in the drafting of international law on prevention of an arms race in outer space including inter alia on the prevention of the placement of weapons in outer space in its capacity as a major space faring nation with proven space technology.
India is not in violation of any international law or Treaty to which it is a Party or any national obligation.
Is the test directed against any country?
The test is not directed against any country. India’s space capabilities do not threaten any country and nor are they directed against anyone.At the same time, the government is committed to ensuring the country’s national security interests and is alert to threats from emerging technologies.
The capability achieved through the Anti-Satellite missile test provides credible deterrence against threats to our growing space-based assets from long range missiles, and proliferation in the types and numbers of missiles.