Hyderabad: World Biofuel Day is observed every year on August 10 in order to create awareness about the importance of non-fossil fuels as an alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
In India, the day is being observed by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas since 2015.
WHY AUGUST 10?
On this day in 1893, Sir Rudolph Diesel (inventor of the diesel engine) for the first time successfully ran mechanical engine with Peanut Oil. His research experiment had predicted that vegetable oil is going to replace fossil fuels in the next century to fuel different mechanical engines. Thus to mark this extraordinary achievement, World Biofuel Day is observed every year on August 10.
WHAT ARE BIOFUELS ?
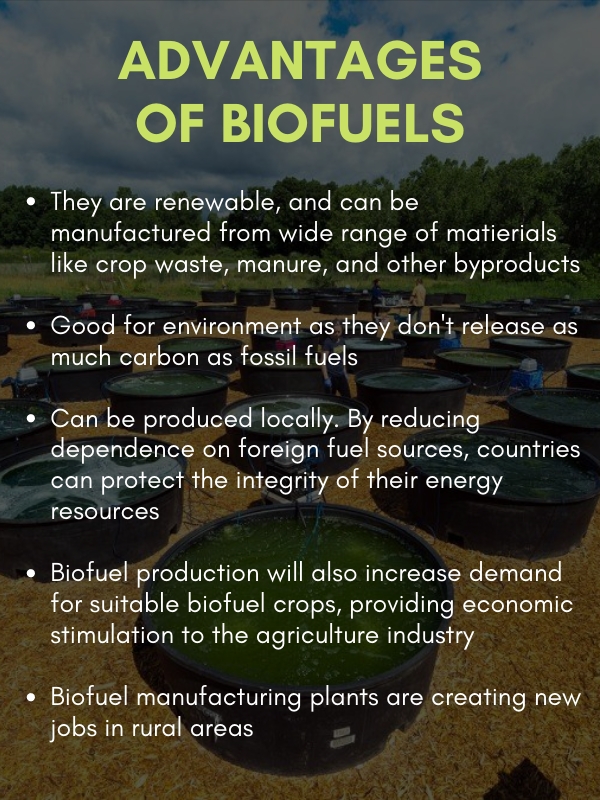
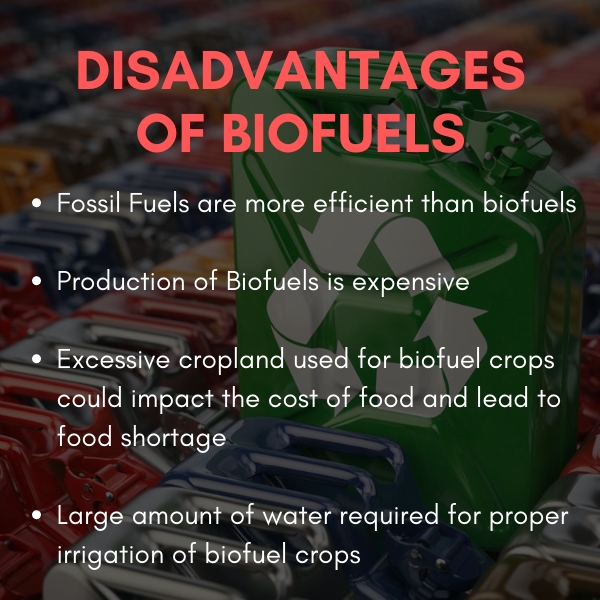
'Biofuels' are fuels produced from renewable resources like biodegradable products, wastes and residues from agriculture, forestry, tree-based oils, other non-edible oils. They are used in place of or in blend with diesel, petrol or other fossil fuels for transport, stationary, and other applications.
MAJOR TYPES OF BIOFUELS
- Bioethanol is derived from corn and sugarcane using fermentation process. A litre of ethanol contains approximately two thirds of the energy provided by a litre of petrol.
- Biodiesel is derived from vegetable oils like soybean oil or palm oil, vegetable waste oils, and animal fats by a biochemical process called 'Transesterification'. It can be used as an alternative for conventional diesel.
- Biogas is produced by anaerobic decomposition of organic matter like sewage from animals and humans. It is commonly used for heating, electricity and for automobiles.
- Biobutanol is produced through the fermentation of starch. The energy content in butanol is the highest among the other gasoline alternatives. It can be added to diesel to reduce emissions.
- Biohydrogen, like biogas, can be produced using a number of processes such as pyrolysis, gasification or biological fermentation. It can be the perfect alternative for fossil fuels.
Read: Biofuels can greatly reduce carbon emissions: Study
INITIATIVES TAKEN BY THE INDIAN GOVERNMENT:
- In october, 2018, Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) scheme was launched to promote use of Compressed Bio Gas (CBG). SATAT initiative envisages establishing 5000 Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) plants across the country by 2023.
- In March, 2019, Government notified the 'Pradhan Mantri JI-VAN (Jaiv Indhan- Vatavaran Anukool fasal awashesh Nivaran) Yojana' for providing financial support to integrated bioethanol projects for setting up second generation ethanol projects in the country using lignocellulosic biomassand other renewable feedstock. The total financial outlay for the scheme is Rs 1969.50 crore for the period 2018-19 to 2023-24.
- Ethanol blending: The 2018 Biofuel Policy has the objective of reaching 20% ethanol-blending and 5% biodiesel-blending by the year 2030.The Government has reduced GST on ethanol for blending in fuel from 18% to 5%.The Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas is making all efforts to increase ethanol supply for petrol.
- GOBAR (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources) DHAN scheme, 2018: It focuses on managing and converting cattle dung and solid waste in farms to useful compost, biogas and bio-CNG, thus keeping villages clean and increasing the income of rural households. It was launched under Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin).
- Repurpose Used Cooking Oil (RUCO) launched by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) aims for an ecosystem that will enable the collection and conversion of used cooking oil to biodiesel.