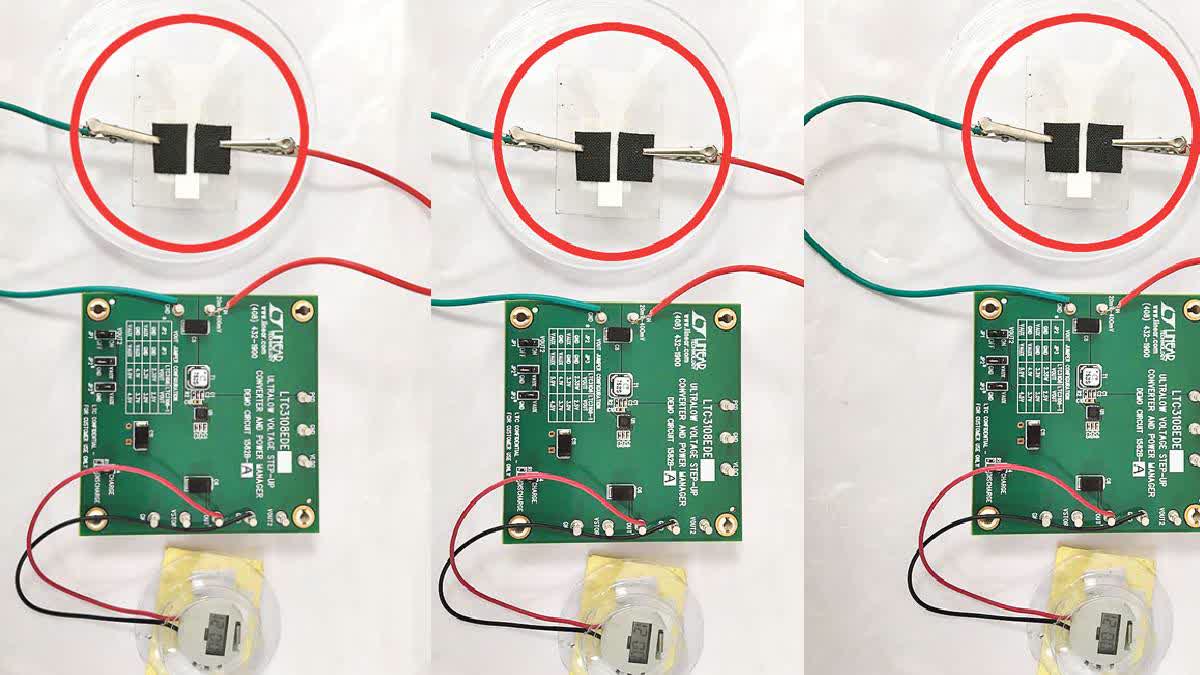
Hyderabad: A team of researchers from Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS) has come up with a unique battery-free 'fuel cell' to power pacemakers, offering a potential solution to the expensive lithium-ion batteries that need frequent replacements.
Professor Sanket Goyal and research student Vanmathi have developed the 'fuel cell' using electro-carbon cloth, marking a significant step towards making pacemakers more affordable and sustainable. This innovation has gained international recognition, making its entry into research journal, 'Micro Mechanics Micro Engineering'.
Why a 'Fuel Cell'?
Pacemakers play a crucial role in managing heart conditions and the lithium-ion batteries are usually relied upon to maintain a steady heart rhythm. However, these batteries not only involve a high manufacturing cost but also require periodic replacement through invasive surgeries. The new fuel cell aims at reducing the overall manufacturing expenses by using electro-carbon as an alternative energy source.
"Traditional pacemaker batteries are costly and have a limited lifespan, requiring frequent replacements. Our fuel cell model provides an affordable alternative, minimising the need for repeated surgeries," Prof Goyal said.
How 'Fuel Cell' operates?
The fuel cell is designed to be powered by blood flow around the heart, generating energy from the body’s natural circulation. When installed in a pacemaker, the fuel cell can provide steady power for 60 to 90 days. Recent animal trials demonstrated the fuel cell’s efficiency, showing it can maintain adequate energy levels to support pacemaker's functioning throughout this period.
"Once the fuel cell reaches its limit, which is around 90 days, it can be safely removed and replaced with a fresh cell," Vanmathi explained. "Our trials have shown that the fuel cell can be re-implanted in the same way as a conventional pacemaker battery replacement."
Advantages:
- Low Cost: By reducing reliance on lithium batteries, the overall cost decreases.
- Reduced Surgical Frequency: The fuel cell replacement will be cheaper, reducing the need for more complex battery replacement surgeries.
- Sustainability: With the body’s natural circulation serving as the energy source, the fuel cell model is an environmental-friendly alternative to traditional batteries.
The team at BITS, Hyderabad plans to expand their research to explore ways of expanding the fuel cell’s lifespan and improving its power efficiency. Future work will focus on optimising this technology to support longer-lasting pacemaker operations, potentially moving toward human clinical trials.
"This research opens up a new approach in cardiac care, especially for those who find the regular surgeries challenging or costly. Our next step involves refining the fuel cell for more extended operation periods, ultimately aiming for practical human applications," Prof Goyal added.
Potential game-changer in cardiac health
If successfully implemented for human use, this fuel cell technology can transform the accessibility and sustainability of pacemaker devices, reducing both financial and physical burdens on patients. With ongoing refinements, the researchers aim to establish a cost-effective, reliable energy source for pacemaker that can benefit countless cardiac patients worldwide.
Read more
New artificial kidney-like device to free patients from dialysis
Delhi doctors implant pacemaker inside brain to control Parkinson's disease