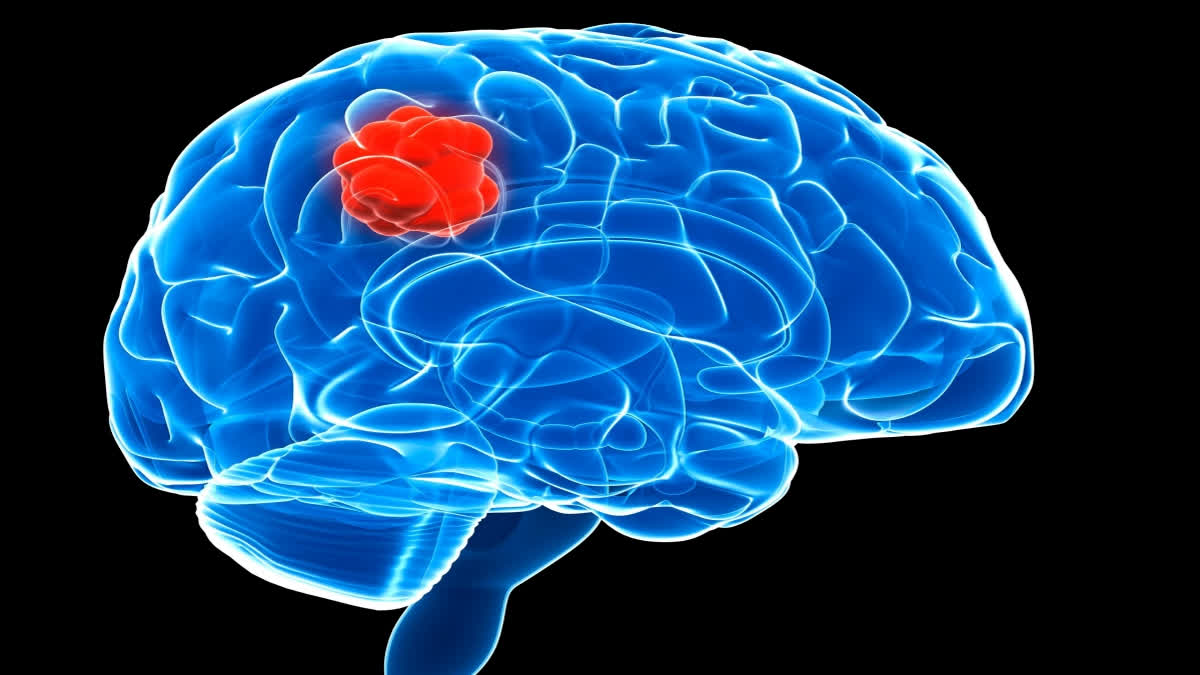
What is Brain Tumor?: Before understanding what a brain tumour is, first, we will learn about the tumor. A tumor is basically an abnormal lump or growth of cells. In the body, there are mainly two main types of tumors namely Benign & Malignant. If the cells in the tumor are normal, it is benign (it means something wrong happened and the cells overgrow and produce a lump). If the cells are abnormal and start growing uncontrollably, then they are cancerous cells, and the tumor is malignant. A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells produce within any part of the brain. The tumor can be benign (non-cancerous) and Malignant (cancerous).
World Brain Tumour Day History: With the objective of finding a cure, encouraging research on the ailment, and spreading awareness about brain Tumors, the German Brain Tumor Association, named Deutsche Hirntumorhilfe eV, initiated a campaign. Tracing back to the early 2000s, World Brain Tumor Day was first observed on June 8, 2000, with the idea of paying tribute to brain Tumor patients and their families by educating people about the disease.
The observance gained international recognition over time, and efforts were made to establish a global day dedicated to brain tumour awareness. The International Brain Tumor Alliance (IBTA), an organisation that brings together brain Tumor advocacy groups from around the world, announced June 8 as World Brain Tumour Day in 2010.
Deaths Due to Brain Tumor: Cancer is among the leading causes of death worldwide and it has accounted for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020 alone. According to a World Health Organisation (WHO) report, the most common cancers are breast cancer; lung cancer; colon and rectum cancer; prostate cancer; skin (non-melanoma) cancer; and stomach cancer. While brain cancer (or brain tumour) is presently not leading cases, the disease is becoming more common each year.
Situation In India: In India, 40,000-50,000 people are diagnosed with a brain tumour every year, according to estimates. Out of these, about 20 percent are children. Experts say that the number could be much higher as many cases, particularly in the rural belts, go unreported. In 2018, brain tumour was found to be the 10th most common kind of tumour among Indians. “The incidence of central nervous system (CNS) tumours in India ranges from 5 to 10 per 100,000 of the population with an increasing trend," says the National Health Portal.
Brain Tumor Symptoms: There are not all symptoms of brain tumours. Meningioma, which is the most well-known brain tumour in grown-ups generally develops gradually and slips by everyone's notice. However, there are still some symptoms to be aware of. These side effects rely on the size of the cancer, the region it influences and how quickly it is developing. Some are as follows:
• Trouble thinking,
• loss of memory,
• confusion, and disorientation
• Personality or behaviour shifts,
• balance problems, such as dizziness,
• Seizures.
Importance of early detection: The expert says that effective therapy depends on early identification. When symptoms become odd or persistent, parents and caregivers should seek medical attention right once. The child's overall prognosis and the effectiveness of treatment can both be greatly impacted by an early diagnosis.
Diagnosis and treatment: To confirm the existence and type of a suspected brain tumour, Dr use a number of methods of diagnosis. The most popular and efficient imaging method is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which produces finely detailed images of the brain.
Biopsy techniques and computed tomography (CT) scans can also be used to get a precise diagnosis. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are frequently used in conjunction for the treatment of paediatric brain tumours. The kind, location, and grade of the tumour will determine the exact course of treatment. Although results have improved with advances in targeted medicines and surgery, the brain's complexity and fragility make therapy still difficult.
Importance of Raising Awareness About Brain Tumor: World Brain Tumor Day plays a critical role in promoting awareness and research. Awareness leads to early detection, which is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Early diagnosis often means more treatment options and a better chance of successful management.
Public awareness campaigns can educate people about the signs and symptoms of brain tumors, encouraging them to seek medical attention promptly. Increased awareness can also reduce the stigma associated with brain tumors, providing much-needed support to patients and their families.