The rise in diabetes prevalence is alarming, with millions affected worldwide. Current estimates suggest that approximately 246 million people are living with diabetes, and projections indicate this figure could soar to 380 million by 2025. This condition not only impacts individual lives but also places a significant burden on healthcare systems globally.
Traditional allopathic approaches primarily focus on insulin and pharmaceutical interventions, which often fail to address the underlying causes of the disease. However, the ancient wisdom of Ayurveda has a holistic approach that helps individuals manage their diabetes more effectively and naturally. By integrating dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and stress management techniques, Ayurveda provides a comprehensive strategy for those seeking to reclaim their health and reduce their dependence on medications. On Ayurveda Day, we got in touch with Dr. Govindarajan, Chief Innovation Officer, Kapiva to know more about how Ayurveda can help manage diabetes.
Dietary guidelines (Ahara)
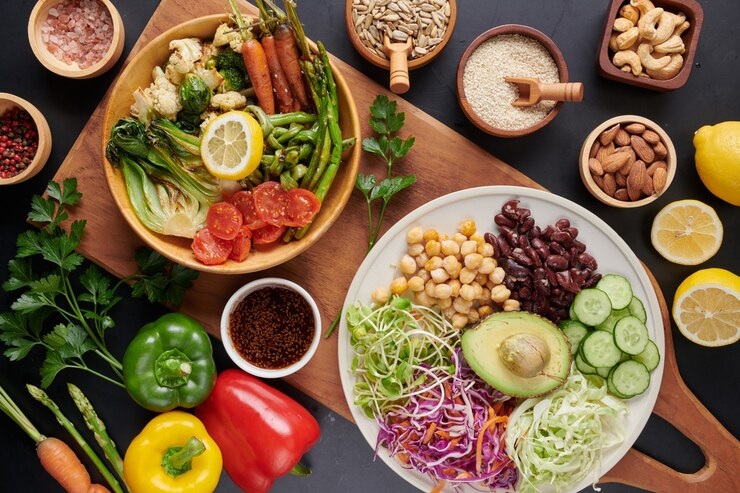

Central to Ayurvedic practice is the idea that food is medicine. One key dietary principle is the focus on low glycemic index (GI) foods. These foods release glucose slowly, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Whole grains, vegetables, Quinoa, Barley, Berries, Chickpeas, nuts & seeds, Leafy Greens and legumes are excellent choices that can be incorporated into daily meals. "By emphasizing these foods, individuals can better control their blood sugar and minimize spikes that contribute to the complications of diabetes," says Dr. Govindarajan.
Eating according to doshas and timings

Ayurveda encourages eating according to one's dosha — a unique combination of physical and mental characteristics. Vata, characterized by air and ether, is often energetic and creative but can be prone to anxiety and dryness. Pitta, dominated by fire and water, is driven and passionate but may experience overheating and irritability. Kapha, composed of earth and water, is grounded and nurturing but can become lethargic or resistant to change. This personalized approach can help individuals select foods that not only support their health but also align with their individual needs. Another important principle is Ayurvedic timing, which recommends making the largest meal of the day during the time when the body's digestive fire (Agni) is at its peak. This practice enhances nutrient absorption and promotes optimal metabolic function.
Lifestyle modifications (Vihara)

In Ayurveda, lifestyle adjustments are as crucial as dietary changes. Establishing a consistent daily routine (Dinacharya) is essential for overall well-being. This routine includes timely meal times, sufficient sleep, and moderate exercise. By creating a structured daily schedule, individuals can improve their body’s rhythm and enhance their insulin sensitivity.
Yoga and pranayama are also vital components of Ayurvedic lifestyle modifications. Practices such as Surya Namaskar (Sun Salutation) not only improve physical fitness but also reduce stress, which can exacerbate diabetes symptoms. Anulom Vilom (alternate nostril breathing) is particularly effective in calming the mind and enhancing respiratory function, further supporting metabolic health.
Panchakarma therapy

For those seeking a more intensive approach, Panchakarma offers a series of detoxification therapies designed to cleanse the body of toxins (Ama) that may contribute to insulin resistance. This traditional Ayurvedic practice involves five therapeutic treatments that can restore balance and vitality.
One of the standout therapies is Basti (medicated enema), which is highly recommended for diabetes management. This treatment helps to balance the Vata dosha and cleanse the colon, considered the root of many ailments in Ayurveda. By purging accumulated toxins, individuals may find significant improvements in their metabolic health.
Evidence and Testimonials
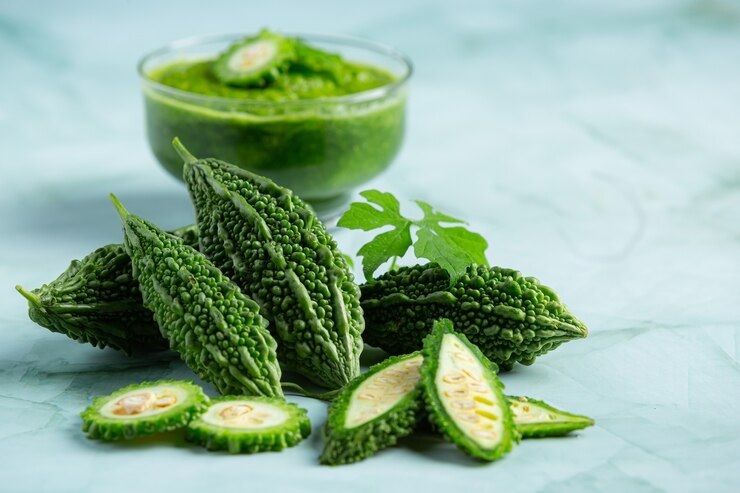

While anecdotal evidence and personal testimonials abound, Dr. Govindarajan states some scientific studies that increasingly support the efficacy of Ayurvedic practices. "Research has shown that specific herbal remedies—such as neem, karela, and amla—possess anti-diabetic properties and can aid in blood sugar regulation. Amla (Indian Gooseberry) is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, enhancing insulin sensitivity. Karela (Bitter Gourd) contains charantin, which can lower blood sugar levels and mimic insulin. Neem is known for its ability to improve insulin sensitivity, while turmeric provides anti-inflammatory benefits through curcumin, potentially reducing blood sugar levels. Fenugreek seeds help lower blood sugar due to their high soluble fiber content, and ginger offers anti-inflammatory properties that may enhance insulin sensitivity. Additionally, ingredients like black cumin (nigella sativa) are known for their ability to improve glucose tolerance. These natural alternatives present a compelling case for integrating Ayurveda into diabetes management."
Ayurveda offers a multifaceted approach to managing diabetes that emphasizes diet, lifestyle, and holistic practices. By reducing dependence on allopathic medicines and embracing natural remedies, individuals can have better health and quality of life.
Read More: