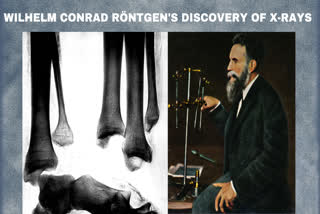
Hyderabad:Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen was born on March 27, 1845, at Lennep in the Lower Rhine Province of Germany, as the only child of a merchant in, and manufacturer of, cloth. His mother was Charlotte Constanze Frowein of Amsterdam, a member of an old Lennep family which had settled in Amsterdam.
When he was three years old, his family moved to Apeldoorn in The Netherlands, where he went to the Institute of Martinus Herman van Doorn, a boarding school In 1862 he entered a technical school at Utrecht, where he was however unfairly expelled, accused of having produced a caricature of one of the teachers, which was in fact done by someone else.
He then entered the University of Utrecht in 1865 to study physics. Not having attained the credentials required for a regular student, and hearing that he could enter the Polytechnic at Zurich bypassing its examination, he passed this and began studies there as a student of mechanical engineering. He attended the lectures given by Clausius and also worked in the laboratory of Kundt. Both Kundt and Clausius exerted great influence on his development.
In 1869 he graduated Ph.D. at the University of Zurich, was appointed assistant to Kundt and went with him to Würzburg in the same year, and three years later to Strasbourg.
- In 1874 he qualified as Lecturer at Strasbourg University and in 1875 he was appointed Professor in the Academy of Agriculture at Hohenheim in Württemberg.
- In 1876 he returned to Strasbourg as Professor of Physics, but three years later he accepted the invitation to the Chair of Physics at the University of Giessen.
- In 1899 he declined an offer to the Chair of Physics in the University of Leipzig, but in 1900 he accepted it in the University of Munich, by special request of the Bavarian government, as the successor of E. Lommel. Here he remained for the rest of his life.
Röntgen’s first work was published in 1870, dealing with the specific heats of gases, followed a few years later by a paper on the thermal conductivity of crystals.