Bilaspur: In an astonishing discovery, rare hafted tools have been unearthed in the Seer Khad valley of Ghumarwin. The antique rare tools belonging to the Paleolithic era have been estimated to be around a lakh-year-old.
Hafting began 3,00,000 years ago when man began hunting attaching a stone tip to a spear. Hafted tools are those tools where a bone, stone or metal is tied to a haft i.e. a string or a handle.
According to Dr Anek Ram Sankhyan, the former senior anthropologist of Anthropological Survey of India, Kolkata, these hafted tools are approximately 1 lakh years old.
Dr Sankhyan estimated the age of these hafted tools with the help of OSL technology. Dr Sankhyan claims that such ancient evidence has been found for the first time in the northwestern sub-Himalayas of India. The discovery of these tools in this area is a testimony to the varied activities of prehistoric humans.
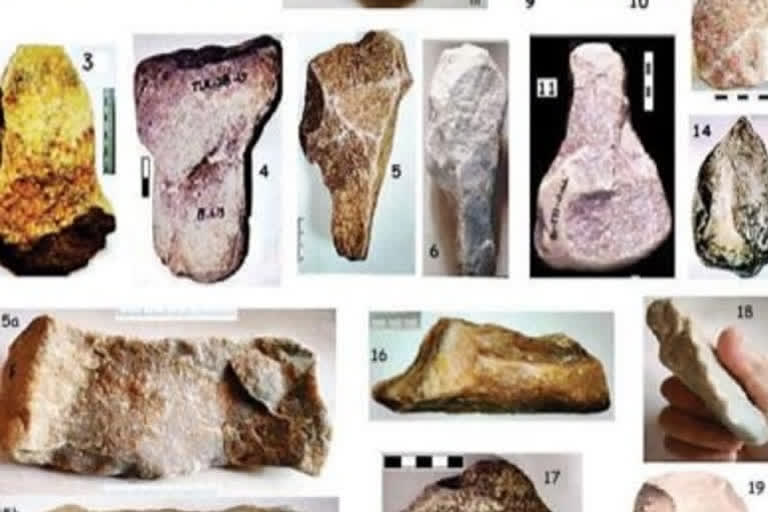
Dr Anek Ram Sankhyan was working for the last 5 years in the Seer Khad valley of Ghumarwin. During this time, he got many important Paleolithic tools which belonged to the primitive man era. They have discovered 450 Middle pre-Palaeolithic tools from the region lying between Ghumarwin to Bam and Jahu.
READ: Congress-ruled states mulling over legal ways to nullify Centre's farm laws
From this recently discovered collection, he has identified 20 categories of tools, including 111 hafted tools. The discoveries also include large-sized axes, spears, arrows, shovels, meat choppers and other tools.
In addition to these tools, from Ghumarwin, very rare saws, hoes, knives, laurel leaves, sharp-edged swords, wooden piercing chisels have also been unearthed. Another device, which looks similar to press tools has also been discovered and it is being speculated that it must have been used to straighten the skins.
Dr Sankhyan told that during the pre-Paleolithic age i.e. around 2 million years ago, the primitive man was accustomed to using hand axes, choppers, scrapers etc., which were used for short-distance hunting. Gradually, the humans learned the art of hunting by throwing weapons to avoid direct encounters with dangerous animals. The idea was to tie them with a wooden pole or handle and much later tools like hammer, axe, spade and shovel were invented.
"Earlier fossils of primitive man were discovered in Harimalyagar of Ghumarwin, which indicate that it was a land of primitive man’s origin. Such discoveries give Devbhumi Himachal a place among the oldest primitive lands of the world," he said, adding that due to paucity of fossil institutions, these invaluable fossils are increasingly becoming a centre of attraction in museums abroad. He also said that these valuable stone tools which are getting destroyed through sand, gravel and stone mining should be preserved.
READ:Chhattisgarh police exhume girl's body months after her 'gangrape'